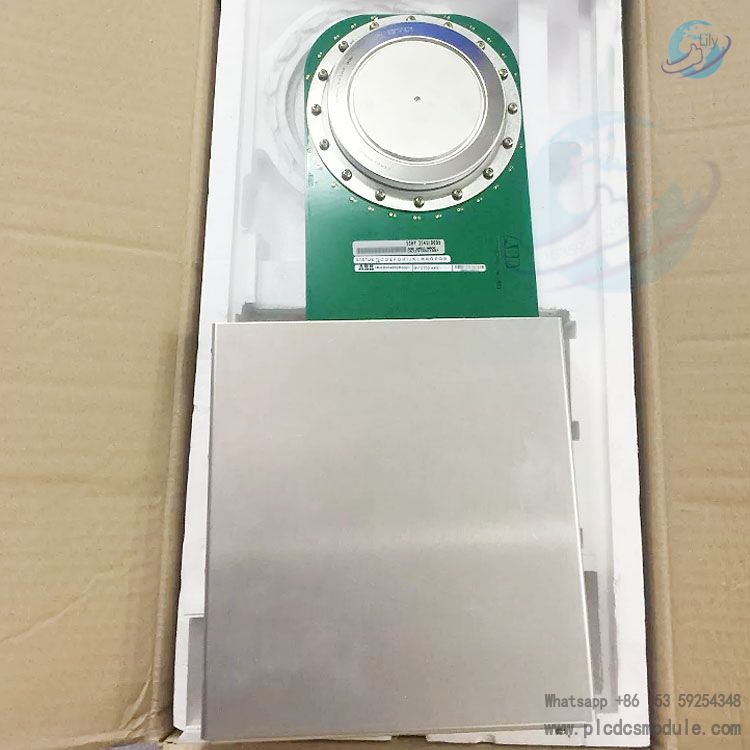
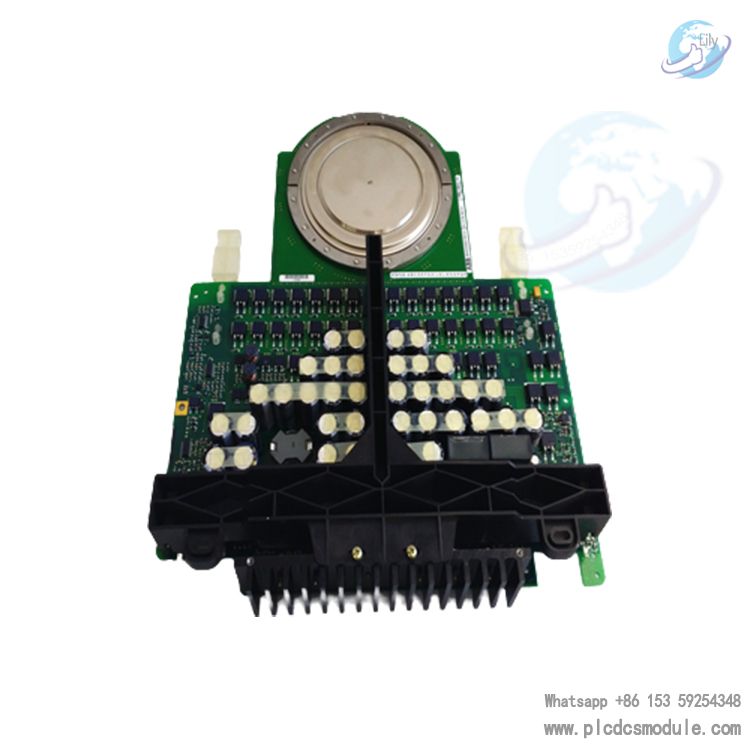
Its core positioning is to act as a signal interaction and local computing hub: it not only enables accurate signal transmission between external devices (sensors, actuators) and master controllers, but also independently performs localized tasks such as analog signal conditioning and logic operations. It is widely suitable for harsh industrial scenarios including cranes, production lines and process control, and delivers outstanding performance especially in applications requiring high reliability, real-time response and anti-interference capability.Integrating ABB’s hardware design expertise and software compatibility advantages in the industrial automation field, this product supports multi-protocol communication, modular integration and flexible configuration. It can be seamlessly integrated into ABB drive systems and third-party automation architectures, satisfying diverse requirements ranging from simple I/O management to complex distributed control.
related documents

Core Positioning and Functional Overview
1. Core Functional Positioning
- Signal Management: It supports bidirectional interaction of digital and analog signals. It can connect to a variety of sensors (input channels) such as thermocouples, pressure transmitters and encoders, and output control signals to actuators (output channels) including contactors, drives and valves, thus achieving a complete control loop of sensing - decision-making - execution.
- Local Computing: Equipped with independent processing capability, it supports basic control algorithms such as arithmetic operations, PID regulation and logic judgment. It can complete local data preprocessing (e.g., signal filtering, linearization correction), reducing the data transmission load of the master controller and improving system response speed (data update cycle ≤ 10ms).
- Cooperative Communication: As a distributed node, it enables real-time communication with ABB PLCs (e.g., AC500 series), DCS systems and drive equipment (frequency converters, servo drives). It supports industrial communication protocols including Modbus TCP, Ethernet/IP and Profibus-DP, and is compatible with the cooperative control architecture of local processing + remote monitoring.
2. Key Differentiated Advantages
- High-reliability Design: Adopting ABB industrial-grade electronic components and stringent manufacturing standards, it supports a storage temperature range of -40°C ~ +85°C and an operating temperature range of 0°C ~ +55°C. It features an IP20 protection rating and electromagnetic interference (EMI) resistance (compliant with the EN 61000-6-2 industrial immunity standard), ensuring stable operation in harsh environments with dust, vibration and voltage fluctuations.
- High-precision Signal Conditioning: Built-in 16th-order low-pass filter circuits and signal amplification modules enable it to achieve an analog acquisition accuracy of ±0.05% of full scale. It can condition weak millivolt-level signals from thermocouples and 4-20mA standard signals from pressure transmitters into stable operational signals, avoiding control errors caused by signal distortion.
- Flexible Scalability: Its modular design supports cascading with up to 127 extension modules, allowing users to increase or decrease the number of I/O channels according to application requirements. Meanwhile, it is compatible with ABB Automation Builder engineering software and supports IEC 61131-3 standard programming languages (LD, FBD, ST, etc.), facilitating flexible development and debugging by engineers based on project needs.
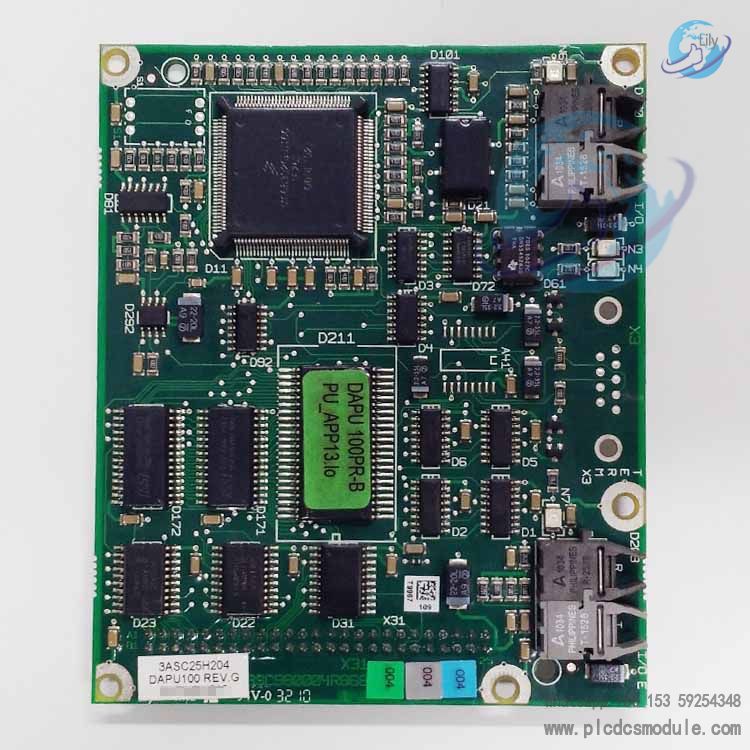

Technical Specifications
1. Basic Parameters
2. I/O Channels and Signal Support
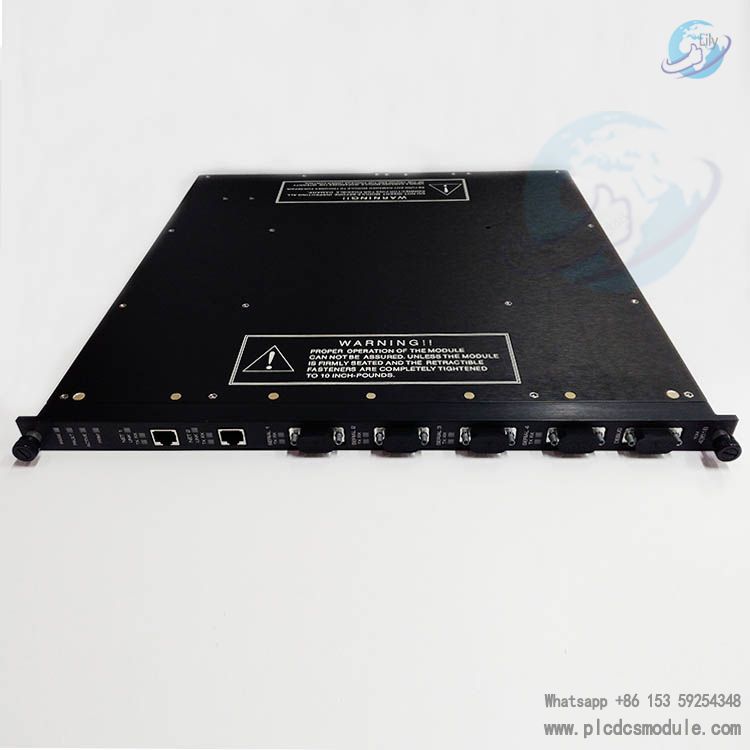
3. Communication Interfaces
Debugging Interface: RS232 port, supporting connection with PCs for program downloading and fault diagnosis (requires dedicated tool cable 3ASC262741H1).

Application Scenarios
- Industrial Automation Production LinesApplication Scenarios: Multi-equipment linkage control for automotive assembly lines and food packaging lines.Functional Roles: Collects conveyor belt speed (encoder signals) and sensor position signals, outputs control signals to servo drives and pneumatic valves, and communicates with the MES system via Ethernet to achieve production data traceability and remote monitoring.Core Advantages: High-precision signal processing ensures synchronous operation of conveyor belts; the distributed architecture reduces wiring complexity; and online debugging support avoids production line downtime.
- Cranes and Material HandlingApplication Scenarios: Hoisting and traveling control of overhead cranes and winches (refer to the ASTAT crane motion controller solution).Functional Roles: Connects to weight sensors (4-20mA signals) and limit switches (dry contact signals), implements overload protection and limit control through local computing, communicates with the ASTAT controller simultaneously, and outputs motor speed control signals.Core Advantages: Vibration and anti-interference design is suitable for the bumpy operating environment of cranes; high reliability ensures the safety of heavy material handling; and support for linkage with the Master-Follower system enables multi-motor synchronization.
- Process Control (Chemical / Power Industry)Application Scenarios: Temperature and pressure control of chemical reactors, and parameter monitoring of steam turbines in thermal power plants.Functional Roles: Collects signals from thermocouples (furnace temperature) and pressure transmitters (reactor internal pressure), outputs control signals to heating rods and control valves through local PID computing, and uploads data to the DCS system at the same time.Core Advantages: High-precision analog signal processing ensures stable process parameters; redundant power supply and fault detection functions improve system safety; and it meets the continuous operation requirements of the chemical and power industries.
- Building and Energy ManagementApplication Scenarios: Central air conditioning system control in buildings and UPS power supply monitoring in data centers.Functional Roles: Collects air conditioning return air temperature (PT100 signals) and UPS output current (4-20mA signals), outputs control signals to fans and water pumps, and connects to the Building Automation System (BAS) via Ethernet.Core Advantages: Modular design is adaptable to buildings of different scales; low power consumption (standby power consumption ≤ 5W) meets energy-saving requirements; and remote diagnosis support reduces on-site maintenance costs.

Installation and Maintenance Recommendations
1. Installation Precautions
- Wiring Requirements: Shielded twisted-pair cables shall be adopted for analog signal transmission, with the shielding layer grounded at one end. To avoid electromagnetic interference, the distance between analog signal cables and power cables shall be no less than 30cm.
- Power Supply Configuration: It is recommended to use a redundant 24V DC power supply (e.g., ABB CP-E series). The cross-sectional area of the power cable shall be at least 1.5mm² to ensure stable power supply.
- Grounding Treatment: The control board must be grounded independently (with a grounding resistance ≤ 4Ω) and separated from the equipment enclosure grounding to prevent ground loop current from interfering with signals.
- Wiring Inspection: Before installation, the I/O channel wiring diagram (refer to Section 2.2 of the ASTAT Manual) shall be checked to ensure correct polarity connection, thus avoiding channel burnout caused by reverse polarity.
Related Products and System Integration
- Compatible ABB Products
- Drive Equipment: ABB ACS880 series frequency converters, ASTAT crane motion controllers (e.g., DARA 1000)
- Control Equipment: ABB AC500 PLCs (PM573/PM583), DCS systems (800xA)
- Sensors and Actuators: ABB pressure transmitters (266 series), encoders (DADT 100), contactors (A series)
- Software Tools: Automation Builder (programming), CMT Tool (parameter configuration and fault diagnosis)
- System Integration Example (Crane Control)
- Architecture Composition: DAPU100 3ASC25H204 (I/O processing) + DARA 1001 (control module) + DAPM 100 (Cabin I/O) + weight sensors + motors
- Data Flow: Weight sensors → DAPU100 analog input → local computing (overload judgment) → output signals to DARA 1001 → control motor start/stop and speed. Meanwhile, data is uploaded to the cab HMI via Profibus-DP.
Core Functions: Enables crane hoisting weight monitoring, overload protection and limit control. The distributed architecture reduces wiring between the cab and the electrical room.
Customers who purchased this product are also browsing the following products:ABB 5SHY3545L0009 3BHB013085R0001 Thyristor Module














 3005319639
3005319639